
What is .NET Framework?
.NET Framework is a software development framework for building and running applications on Windows.
.NET Framework is part of the .NET platform, a collection of technologies for building apps for Linux, macOS, Windows, iOS, Android, and more.
The .NET Framework is a software development platform that was introduced by Microsoft in the late 1990 under the NGWS. On 13 February 2002, Microsoft launched the first version of the .NET Framework, referred to as the .NET Framework 1.0.
.NET and .NET Framework
.NET is a developer platform made up of tools, programming languages, and libraries for building many different types of applications.
There are various implementations of .NET. Each implementation allows .NET code to execute in different places—Linux, macOS, Windows, iOS, Android, and many more.
- .NET Framework is the original implementation of .NET. It supports running websites, services, desktop apps, and more on Windows.
- .NET is a cross-platform implementation for running websites, services, and console apps on Windows, Linux, and macOS. .NET is open source on GitHub. .NET was previously called .NET Core.
- Xamarin/Mono is a .NET implementation for running apps on all the major mobile operating systems, including iOS and Android.
.NET Standard is a formal specification of the APIs that are common across .NET implementations. This allows the same code and libraries to run on different implementations.
Key takeaways
- The .NET Framework is an open-source platform for developing Windows-based applications, often referred to as Microsoft .net
- The .NET Framework includes a variety of developer tools and class libraries
- The .NET Framework works with applications developed in C#, F#, Visual Basic, and other popular programming languages
- You can use the .NET Framework to develop both web-based and forms-based apps, as well as apps that integrate with major database platforms
Architecture of .NET Framework
The two major components of .NET Framework are the Common Language Runtime and the .NET Framework Class Library.
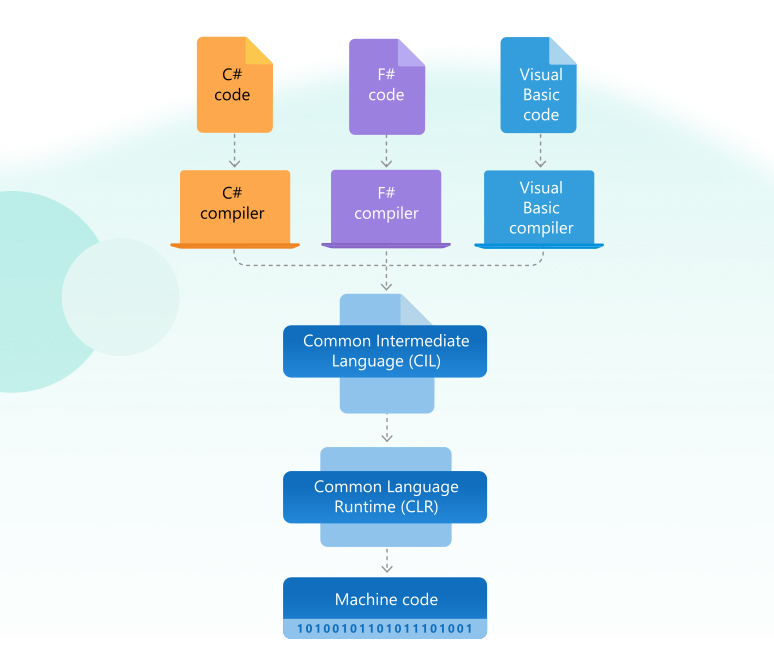
The .NET Framework architecture provides an execution environment that integrates a variety of compatible programming languages. In essence, the architecture works like this:
- An application is written in one of a variety of compatible programming languages (the most popular being C#, F#, and Visual Basic)
- The application is compiled to the Common Intermediate Language (CIL)
- The Common Language Runtime (CLR) executes the application on the user's machine, converting the CIL to machine code
Essential components of the .NET Framework
There are several essential components of the .NET Framework, including the Framework Class Library, the Common Intermediate Language and the Common Language Runtime.
01. CLR [Common Language Runtime]
The Common Language Runtime (CLR) is the Framework's execution engine. It executes the CIL code by converting it into machine languages. In addition to running the applications, it includes a variety of useful services, including:
- Exception handling
- Garbage collection (removes unneeded resources)
- Thread management
- Type safety
02. Framework Class Library
The .NET Framework includes a set of standard class libraries. A class library is a collection of methods and functions that can be used for the core purpose.
For example, there is a class library with methods to handle all file-level operations. So there is a method which can be used to read the text from a file. Similarly, there is a method to write text to a file.
Most of the methods are split into either the System.* or Microsoft.* namespaces. (The asterisk * just means a reference to all of the methods that fall under the System or Microsoft namespace).
The Framework Class Library (FCL) provides a variety of APIs and types that provide common functionality across apps. There are APIs for:
- Reading files
- Writing files
- Connecting to databases
- Types are provided for strings, numbers, dates, etc.
03. Common Intermediate Language
The Common Intermedia Language (CIL) stores code created by the source compliers. The compiled code is stored in files with a .DLL or .EXE extensions.
App models in the .NET Framework
The .NET Framework supports a number of app models for building software applications. The most popular include:
- ADO.net: used to develop applications that interact directly with databases, such as Microsoft SQL Server
- ASP.Net: used to develop web-based applications that are served over the Internet and run inside users' web browsers
- WinForms: used to develop forms-based applications that run on users' computers
11 Programming Languages which are designed and developed by Microsoft are:
- C#.NET
- VB.NET
- C++.NET
- J#.NET
- F#.NET
- JSCRIPT.NET
- WINDOWS POWERSHELL
- IRON RUBY
- IRON PYTHON
- C OMEGA
- ASML(Abstract State Machine Language)
Advantages of .NET Framework:
The .NET Framework has become ubiquitous in the programming world, especially in the development of web-based and business applications. It was ranked the "most loved" framework in the 2020 Stack Overflow Development Survey, used by 71.5% of developers in the survey.
This ongoing popularity is because .NET Framework offers multiple benefits to developers, including the following ten:
01. Language compatibility
The .NET Framework works with a wide variety of programming languages, including: C++, C#, F# …
Developers can work in their language of choice and know that it's compatible with the .NET Framework.
02. Cross-platform compatibility
Unlike some other frameworks, older versions of .NET Framework are fully compatible with more recent versions. The old code works just fine when .NET upgrades—o modifications are necessary.
03. Portability
Applications built on the .Net framework can be made to work on any Windows platform. And now in recent times, Microsoft is also envisioning to make Microsoft products work on other platforms, such as iOS and Linux.
04. Speed
Another thing that developers like about .NET and the .NET Framework is that they're fast—really fast.
05. Memory management
The .NET Framework uses the Common Language Runtime for application memory management. The CLR automatically identifies and closes unused system resources to free up memory at regular intervals.
06. Reliability
.NET Framework benefits from decades of use and development. Its reliability in running thousands of custom applications is unsurpassed.
07. Easy deployment
.NET Framework is also easy to deploy. The framework offers a variety of tools developers can use to package .NET applications. When these packages are distributed, they automatically install the application. Most developers use Microsoft’s Visual Studio to code in .NET, but it also works in many IDE and code editors.
08. Large class library
The .NET Framework comes with a large class library of pre-tested code that developers can use in their apps. This Framework Class Library helps to increase developer productivity and minimize development time.
09. Side-by-side execution
Because the .NET Framework enables multiple versions of the Common Language Runtime to run on the same machine, developers can run different app versions side-by-side. This enables a comparison of different versions and eases troubleshooting.
10. Security
.NET Framework validates apps before granting access to the app or its source code. This results in an extremely secure development environment and apps that are more resistant to malicious actions.