
C# if Statement
Several decision-making statements are available in C# where certain logical conditions are required to flow a program continuously.
The decision-making statements included in C# are: if statement, if-else statement, switch statement, and ternary operator.
The if statement is perhaps the most basic of flow control options available to the C# programmer.
The if statement checks the given condition. If the condition evaluates to be true then the block of code/statements will execute otherwise not.
Programmers who are familiar with C, C++ or Java will immediately be comfortable using C# if statements.
1 - Syntax of C# if Statement
The C# if statement tests the condition. It is executed if condition is true.
if (condition)
statement;*** Note that if is in lowercase letters. Uppercase letters (If or IF) will generate an error.
If you want to execute multiple statements, you need to use a block { } like this:
if (condition)
{
// block of code to be executed if the condition is True
}However, it’s a good practice to always use a block with the if statement even though it has a simple statement.
Note: If the curly brackets { } are not used with if statements then the statement just next to it is only considered associated with the if statement.
Example:
if (condition)
statement 1;
statement 2;In this example, only statement 1 is considered to be associated with the if statement.
2 - C# Conditions and If Statements
C# supports the usual logical conditions from mathematics:
- Less than:
a < b - Less than or equal to:
a <= b - Greater than:
a > b - Greater than or equal to:
a >= b - Equal to:
a == b - Not Equal to:
a != b
You can use these conditions to perform different actions for different decisions.
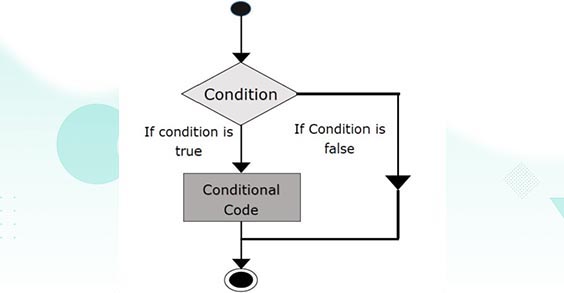
3 - C# If Statement Flow Chart Diagram
The following flowchart illustrates how the C# if statement works:
4 - C# if statement examples
Let’s take some examples of using the if statement.
01. Example 1
if (5 < 2 * 3) {
Console.WriteLine ("true"); // true
}The statement can be a code block:
if (5 < 6) {
Console.WriteLine ("true");
Console.WriteLine ("Let's move on!");
} 02. Example 2
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* local variable definition */
int a = 10;
/* check the boolean condition using if statement */
if (a < 20)
{
/* if condition is true then print the following */
Console.WriteLine("a is less than 20");
}
Console.WriteLine("value of a is : {0}", a);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result:
