
C# Value and Reference Types
In c#, we have two ways to allocate the space in memory, i.e., either on stack or heap memory based on the Value Type or Reference Type parameters.
This seems to be a basic but very important part of C# programming.
1 - C# Value type
Value types are generally (not always) stored on the stack and are passed by copying.
The way in which a variable assignment works differs between reference and value types.
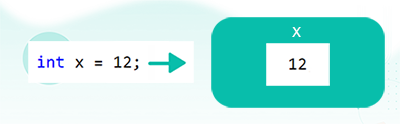
For example, if we define and assign a value to the variable like int x = 12; then the system will use the same memory space of variable ‘x’ to store the value ‘12’.
The following data types are all of value type:
int | float | long | char | bool | byte | decimal | double |
enum | sbyte | short | struct | uint | ulong | ushort | |
If we have something like:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int v1 = 12;
int v2 = 22;
v2 = v1;
Console.WriteLine(v2);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Output:

Implementation:
Here, both v1 and v2 will be on the stack and are different entities.
2 - C# Reference Type
A value type is basically stored on the heap and passed by creating a reference.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class A
{
public int value
{
get;
set;
}
public A(int passbyref)
{
this.value = passbyref;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
A v1 = new A(12);
A v2 = new A(22); //Breakpoint
v2 = v1;
Console.WriteLine(v1.value);
Console.WriteLine(v2.value);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:

Implementation:
v1 and v2 will be on the heap as two entities until a breakpoint.
And after the breakpoint, they both point to one entity.
So, a change in one will affect the other.
The following are the different data types that will fall under Reference Type in c# programming language.
- String
- Class
- Delegates
- All Arrays, Even if their elements are value types
3 - C# Passing Arguments
We have the following four possibilities:
- Pass value type by value.
- pass value type by reference
- pass reference type by value.
- pass reference type by reference.
3. 01 - C# Pass value type by value
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
struct A
{
public int val
{
get;
set;
}
}
class Program
{
public static void methodtoshowref(A obj)
{
obj = new A();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
A v1 = new A();
v1.val = 10;
methodtoshowref(v1);
Console.WriteLine(v1.val);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:

10 : because one more copy is created and thus the original is not affected.
3. 02 - C# Pass value type by reference
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
struct A
{
public int val
{
get;
set;
}
}
class Program
{
public static void methodtoshowref(ref A obj)
{
obj = new A();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
A v1 = new A();
v1.val = 10;
methodtoshowref(ref v1);
Console.WriteLine(v1.val);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Output:

0 : since now one copy is shared by both methods.
3. 03 - C# Pass reference type by value (by default)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class A
{
public int val
{
get;
set;
}
}
class Program
{
public static void methodtoshowref(A obj)
{
obj = null;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
A v1 = new A();
v1.val = 10;
methodtoshowref(v1);
Console.WriteLine(v1.val);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Output:

10 : this happens because we are passing it by value.
*** Now here if we do, obj.val=1000 then it will print 1000 (this is because passing a variable to a function by value is equivalent to instantiating a new variable and assigning it to the first).
3. 04 - C# Pass reference type by reference
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class A
{
public int val
{
get;
set;
}
}
class Program
{
public static void methodtoshowref(ref A obj)
{
obj = null;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
A v1 = new A();
v1.val = 10;
methodtoshowref(ref v1);
Console.WriteLine(v1.val);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
An unhandled exception of type 'System.NullReferenceException' occurred in HelloWorld.exeThe error we have now is obj=null so it will give a nullobject error.
Related Tutorials:
- C# Data Types
- C# Variables
- C# Types of Variables
- C# Integer Variable Types
- C# Floating Point Variables
- C# Boolean Variable Type
- C# Character Variable Type
- C# String Variables
- C# Casting Variable Types
- C# Implicitly Typed Local Variable: C# Var keyword
- C# Keywords
- C# Comments
- C# Parameters
- C# Constants
- C# Numeric Types
- C# Numeric Value
- C# User Input