
C# Multidimensional Arrays
1 - Introduction to C# multidimensional arrays
Multidimensional arrays come in two varieties: rectangular and jagged.
Rectangular arrays represent an n-dimensional block of memory, and jagged arrays are arrays of arrays.
When an array has more than one dimension, it is called a multidimensional array.
The following example declares a two-dimensional array (or 2D array) of two rows and three columns:
int [,] matrix = new int[2, 3];The comma (,) inside the square brackets denotes the number of dimensions. If you want to declare a three-dimensional array (or 3D array), you can use two commas (,) like this:
int[,,] tensor = new int[3, 3, 3];The multidimensional array is also known as rectangular arrays in C#. It can be two dimensional or three dimensional. The data is stored in tabular form (row * column) which is also known as matrix.
For example:
int[,] arr=new int[3,3];//declaration of 2D array
int[,,] arr=new int[3,3,3];//declaration of 3D array
2 - Initializing C# multidimensional arrays
There are two ways to shorten array initialization expressions.
The first is to omit the new operator and type qualifications:
char[] vowels = {'a','e','i','o','u'};
int[,] rectangularMatrix = {
{0,1,2},
{3,4,5},
{6,7,8}
};
int[][] jaggedMatrix = {
new int[] {0,1,2},
new int[] {3,4,5,2,2,2,2},
new int[] {6,7,8}
}; The second approach is to use the var keyword, which tells the compiler to implicitly type a local variable:
var i = 3; // i is implicitly of type int
var s = "asdf"; // s is implicitly of type string
var rectMatrix = new int[,]{
{0,1,2},
{3,4,5},
{6,7,8}
};
var jaggedMatrix = new int[][]{
new int[] {0,1,2},
new int[] {3,4,5},
new int[] {6,7,8}
}; We can omit the type qualifier after the new keyword and have the compiler infer the array type:
var letters = new[] {'a','e','i','o','u'}; // Compiler infers char[]
3 - Rectangular arrays
Rectangular arrays are declared using commas to separate each dimension.
The following declares a rectangular two-dimensional array, where the dimensions are 3 by 3:
int[,] matrix = new int[3,3]; The GetLength method of an array returns the length for a given dimension starting at 0:
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.GetLength(0); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix.GetLength(1); j++) {
matrix[i,j] = i * 3 + j;
}
}A rectangular array can be initialized as follows:
int[,] matrix = new int[,] {
{0,1,2},
{3,4,5},
{6,7,8}
};
4 - C# Jagged arrays
Jagged arrays are declared using successive square brackets to represent each dimension.
Here is an example of declaring a jagged two-dimensional array, where the outermost dimension is 3:
int[][] matrix = new int[3][]; The inner dimensions aren't specified in the declaration, each inner array can be an arbitrary length.
Each inner array is implicitly initialized to null rather than an empty array.
Each inner array must be created manually:
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.Length; i++) {
matrix[i] = new int[3]; // Create inner array
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[i].Length; j++)
matrix[i][j] = i * 3 + j;
}
}A jagged array can be initialized as follows:
int[][] matrix = new int[][] {
new int[] {0,1,2},
new int[] {3,4,5},
new int[] {6,7,8,9}
}; Example:
The following example illustrates using a jagged array:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* a jagged array of 5 array of integers*/
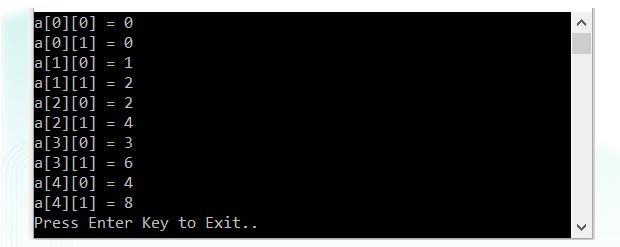
int[][] a = new int[][] { new int[] { 0, 0 }, new int[] { 1, 2 }, new int[] { 2, 4 }, new int[] { 3, 6 }, new int[] { 4, 8 } };
int i, j;
/* output each array element's value */
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine("a[{0}][{1}] = {2}", i, j, a[i][j]);
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Press Enter Key to Exit..");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Output:
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result:
5 - C# Accessing array elements
To access an element in the multidimensional array, you use a comma-separated list of dimensions inside the square brackets. The first dimension starts at zero.
For example, the following example accesses the row 0 column 1 of a two-dimensional array:
array2D[0,1]Similarly, you can specify the dimensions in a 3D array like this:
array3D[0,1,2]The following example shows how to access the elements at row 0 column 0 and row 1 and column 2 of a 2D array:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[,] matrix = {
{1,2,3},
{4,5,6},
{7,8,9},
};
// row 0 column 0
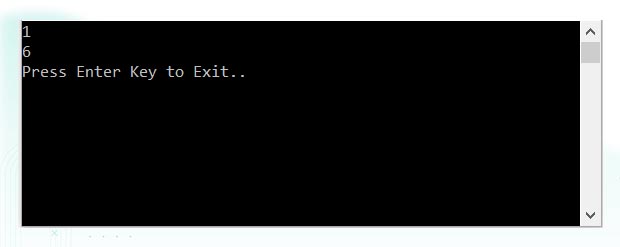
Console.WriteLine(matrix[0, 0]); // 1
// row 1 column 2
Console.WriteLine(matrix[1, 2]); // 6
Console.WriteLine("Press Enter Key to Exit..");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Output:
6 - C# Getting dimension length
The GetLength method of an array returns the length of a dimension. The first dimension starts at zero. The following example declares a 2D array, initialize its elements, and output all the elements to the console:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
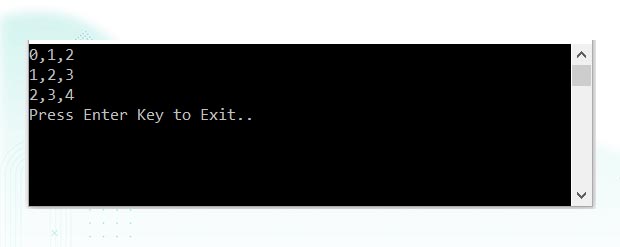
int[,] matrix = new int[3, 3];
// assign integers to the 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < matrix.GetLength(1); j++)
{
matrix[i, j] = i + j;
}
}
// output the 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < matrix.GetLength(1); j++)
{
Console.Write($"{matrix[i, j]}");
Console.Write(j < matrix.GetLength(1) - 1 ? "," : "");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.WriteLine("Press Enter Key to Exit..");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
7 - C# Multidimensional Array Example
Example #1
Let's see a simple example of multidimensional array in C# which declares, initializes and traverse two dimensional array.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
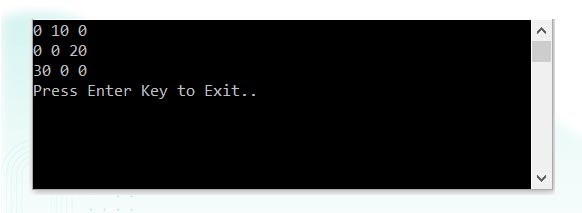
int[,] arr = new int[3, 3];//declaration of 2D array
arr[0, 1] = 10;//initialization
arr[1, 2] = 20;
arr[2, 0] = 30;
//traversal
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
Console.Write(arr[i, j] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();//new line at each row
}
Console.WriteLine("Press Enter Key to Exit..");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
Example #2
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
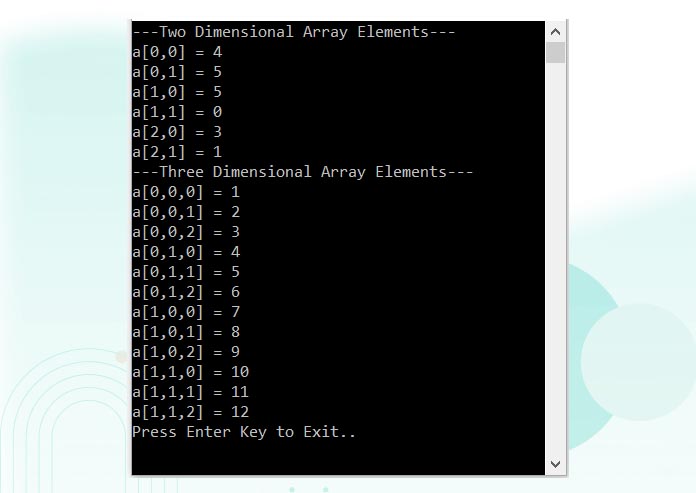
// Two Dimensional Array
int[,] array2D = new int[3, 2] { { 4, 5 }, { 5, 0 }, { 3, 1 } };
// Three Dimensional Array
int[,,] array3D = new int[2, 2, 3] { { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } }, { { 7, 8, 9 }, { 10, 11, 12 } } };
Console.WriteLine("---Two Dimensional Array Elements---");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine("a[{0},{1}] = {2}", i, j, array2D[i, j]);
}
}
Console.WriteLine("---Three Dimensional Array Elements---");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++)
{
Console.WriteLine("a[{0},{1},{2}] = {3}", i, j, k, array3D[i, j, k]);
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Press Enter Key to Exit..");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
8 - Advantages & Disadvantages
Below are the advantages and disadvantages of C# Multidimensional Arrays:
Advantages
- Multidimensional arrays can be used to organize subgroups of data within an array; multidimensional arrays can also be used to store data memory addresses in a pointer array.
- In the program, multidimensional arrays have a static size and initialization at the beginning. Any extension in size shall require the relevant size to be specified during initialization.
- Multidimensional arrays enable performing matrix operations and maintaining large data values under the same variable allocation.
- Multidimensional arrays are used to implement stacks, heaps and Queues, and hash tables.
Disadvantages
- The elements are located in contiguous memory locations for an array; hence any insertion and deletion of an element shall be more complex than similar operations on single elements.
- Also, the elements cannot be inserted into the middle of an array.
- Static allocation can cause wastage and failure to release unused memory if it allocates more memory than necessary. This can have a negative impact.
- Multidimensional arrays can be slower when compared to their single-dimensional array counterparts, which is a major disadvantage. To overcome this, we can replace jagged arrays with multidimensional arrays.