
C# String Variables
A String data type is used to work with String values. In C#, the datatype is denoted by the keyword ‘String’. Below is an example of this datatype.
The string keyword is an alias for the System.String type. Therefore, the string and String are equivalent.
In the preceding section we looked at storing individual characters in a char variable. Whilst this works for storing a single letter or number it is of little use for storing entire words or sentences. For this purpose the string variable type is supported by C#. Variables of type string can store a string of any number of characters.
The string type literals are enclosed in (“”)/ double quotes and also can be started with @””. Long lines can be broken into multiple lines with string literals and be separated by using blank spaces.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
String s = "Hello From XDevSpace!";
String s2 = @"Hello From XDevSpace!";
Console.WriteLine(s);
Console.WriteLine(s2);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Output:
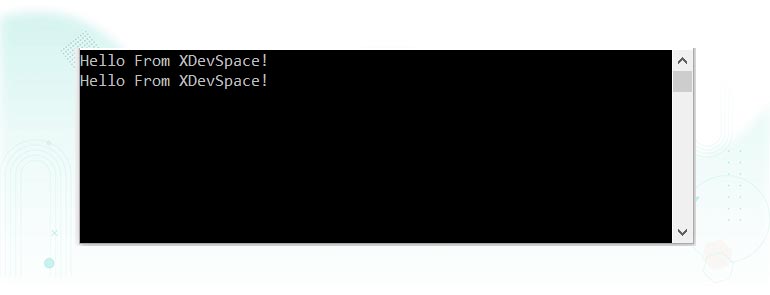
A string declaration in C# cannot be spread over multiple lines. If a string needs to be split over multiple lines by new lines the \n special character can be used. For example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string myString = "This is line one\nThis is line two\nThis is line three";
Console.WriteLine(myString);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
The above example code will result in the following output:
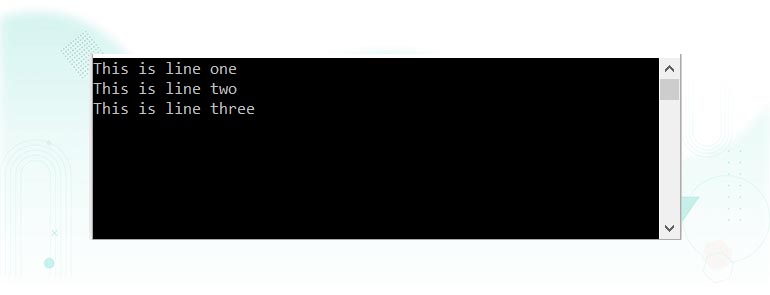
As a matter of fact, any of the special characters outlined in the preceding section on the char type may be embedded into string.
C# Declare a string
The following example declares a string variable without initializing it:
string msg;The following example declares and initializes the string using one statement:
string msg= "Hi from XDevSpace";To create a zero-length string, you use the String.Empty like this:
string msg= String.Empty;It’s equivalent to the following:
string msg = "";
C# Get the length of a string
A string has the Length property that returns the length of a string. To access the Length property, you use the dot operator (.) like this:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string msg = "Hello world from XDevSpace";
Console.WriteLine("msg Length is :"+msg.Length);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
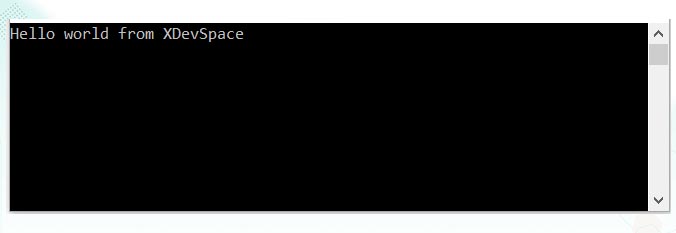
}Output:

C# Concatenate two strings
To concatenate two strings into one, you use the + operator.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string msg = "Hello world"+ " from XDevSpace";
Console.WriteLine(msg);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
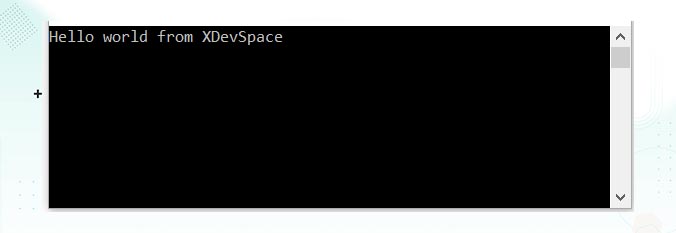
}Output:
C# string is immutable
C# string is immutable. It means that when you make any changes to a string, you’ll always get a new string.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string msg = "Hello world";
msg += " from XDevSpace";
Console.WriteLine(msg);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Output:
Code Explanation:
- First, define the
msgstring variable and initialize it to the string literal "Hello world". - Second, concatenate the
msgstring variable with another string literal "from XDevSpace". - Third, show the
msgstring to the console.
When concatenating the msg with the " string", C# doesn’t change the original string msg but creates a new string that holds the concatenated string.
C# Special Characters (C# Escape sequences)
A text in the real world can include any character. In C#, because a string is surrounded with double quotes, it cannot include " in a string. The following will give a compile-time error.
C# includes escaping character \ (backslash) before these special characters to include in a string.
Use backslash \ before double quotes and some special characters such as \,\n,\r,\t, etc. to include it in a string.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
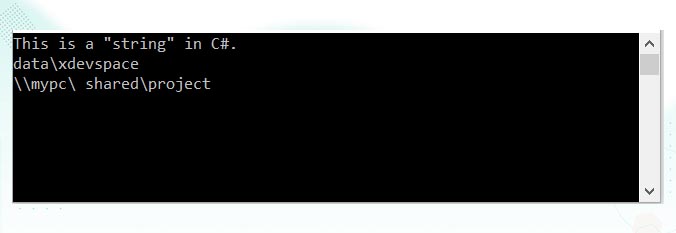
string text = "This is a \"string\" in C#.";
string str = "data\\xdevspace";
string path = "\\\\mypc\\ shared\\project";
Console.WriteLine(text);
Console.WriteLine(str);
Console.WriteLine(path);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Output:
C# Accessing individual characters
Internally, C# stores a string as a collection of read-only characters. To access an individual character in a string, you use the square bracket notation [] with an index: s[index]
The first character has an index of 0. The second character has an index of 1, and so on.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string msg = "Hello";
Console.WriteLine(msg[0]); // H
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:

Because a string is immutable, you can only read individual characters from it.
C# Verbatim string
It is tedious to prefix \ to include every special characters. Verbatim string in C# allows a special characters and line brakes. Verbatim string can be created by prefixing @ symbol before double quotes.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
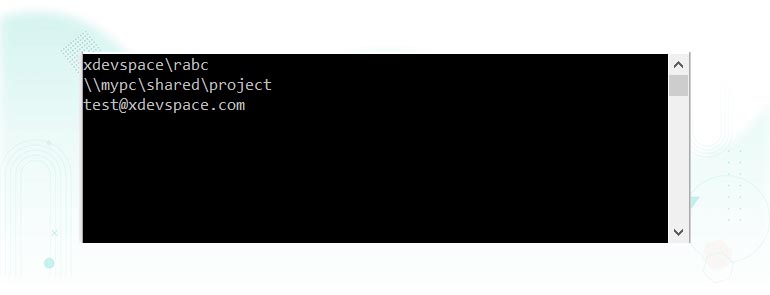
string str = @"xdevspace\rabc";
string path = @"\\mypc\shared\project";
string email = @"[email protected]";
Console.WriteLine(str);
Console.WriteLine(path);
Console.WriteLine(email);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Output:
The @ symbol can also be used to declare a multi-line string.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string method1 = "this is a \n" +
"multi line \n" +
"string";
// Use Verbatim string
string method12 = @"this is a
multi line
string";
Console.WriteLine(method1);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine(method12);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Output:

Please note that you cannot use a backslash to allow " in a varbatim string. If you wish to include @, then use double double-quotes "" to include " in a verbatim string.
string text = "This is a \"string\" in C#."; // valid
string text = @"This is a "string." in C#."; // error
string text = @"This is a \"string\" in C#."; // error
string text = @"This is a ""string"" in C#."; // valid
C# String Interpolation
String interpolation is a better way of concatenating strings. We use + sign to concatenate string variables with static strings.
C# includes a special character $ to identify an interpolated string. An interpolated string is a mixture of static string and string variable where string variables should be in {} brackets.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
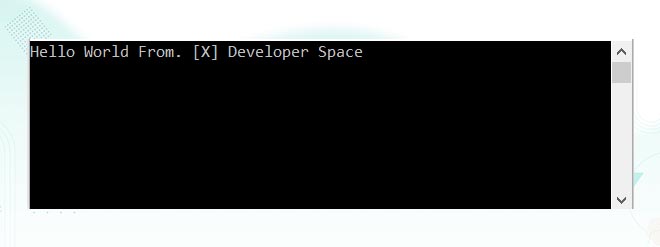
string str1 = "[X]";
string str2 = "Developer";
string str3 = "Space";
string fullString = $"Hello World From. {str1} {str2} {str3}";
Console.WriteLine(fullString);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Output:
In the above example of interpolation, $ indicates the interpolated string, and {} includes string variable to be incorporated with a string.
Use two braces, "{{" or "}}" to include { or } in a string.
Related Tutorials:
- C# Data Types
- C# Variables
- C# Types of Variables
- C# Integer Variable Types
- C# Floating Point Variables
- C# Boolean Variable Type
- C# Character Variable Type
- C# Casting Variable Types
- C# Implicitly Typed Local Variable: C# Var keyword
- C# Keywords
- C# Comments
- C# Parameters
- C# Constants
- C# Value and Reference Types
- C# Numeric Types
- C# Numeric Value
- C# User Input