
C# Ternary operator
C# uses something called a ternary operator to provide a shortcut way of making decisions.
The syntax of the ternary operator is as follows:
[condition] ? [true expression] : [false expression]The way this works is that [condition] is replaced with an expression that will return either true or false.
If the result is true then the expression that replaces the [true expression] is evaluated. Conversely, if the result was false then the [false expression] is evaluated.
Let's see this in action:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 10;
int y = 20;
Console.WriteLine(x > y ? x : y);
// output = 20
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}The above code example will evaluate whether x is greater than y. Clearly this will evaluate to false resulting in y being returned to the WriteLine method for display to the user.
C# Ternary operator has the form: q ? a : b => if condition q is true, a is evaluated, else b is evaluated.
For example the following code use ternary to get the bigger value of two.
int Max (int a, int b)
{
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}We can use the if statement to code the same logic:
if(a > b){
return a;
}else{
return b;
}1 - Comparison of Two Values Using If Else
Consider the below C# program for comparison of two values using the if-else statement:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 40;
int b = 50;
if (a < b)
{
Console.WriteLine("a's value is less than b");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("b's value is less than a");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
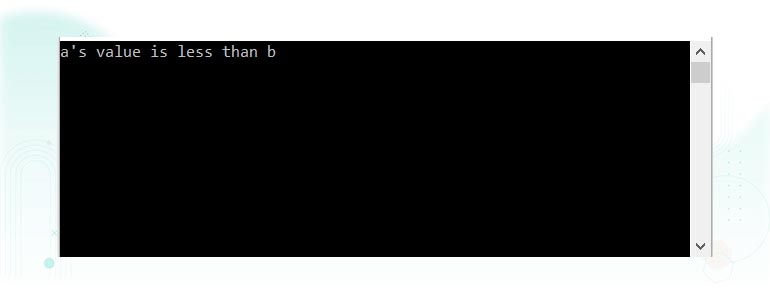
In the above program, two variables, a and b, are defined and assigned some values. Their values are compared against each other to find out which is greater using if-else conditional statements.
2 - Comparison of Two Values Using Ternary Operators
Consider the below C# program for comparison of two values using ternary operators.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 40;
int b = 50;
Console.WriteLine((a < b) ? "a's value is less than b" : "b's value is less than a");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
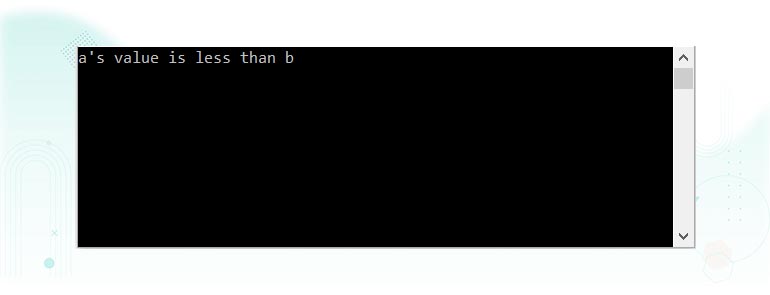
- In the above program, two variables,
aandb, are defined and assigned some values. - Their values are compared against each other to find out which is greater using ternary operators.
- The conditional statement is executed, and the result of the statement is assigned to a variable res.
- If the conditional statement’s result is
true, the second statement after the ‘?’, which is a’s value is more than b, is printed; otherwise, the third statement after the ‘:’ b’s value is less than a is printed.
3 - Nested Ternary Operator
When the second argument or the third argument after ‘?’ or after ‘:’ is a conditional statement again, then the operator is called the nested ternary operator.
For example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
Console.WriteLine(a > b ? "a's value is more than b" : a < b ? "a's value is less than b" : a == b ? "C" : "No result");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}Output:
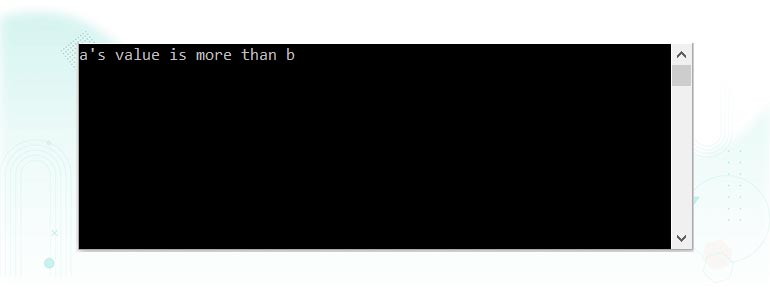
In the above program, two variables, a and b, are defined and assigned some values.
Their values are compared against each other to find out which is greater or if they are equal using ternary operators in C#.
The conditional statement is executed, and the result of the statement is assigned to a variable res.
If the result of the conditional statement is true, the second statement after the ‘?’ which is again a conditional statement a<b is executed, the result of which is assigned to either a’s value is less than b statement before ‘:’ or another conditional statement a==b is executed which is again a conditional statement. The result of this expression prints a’s value is less than b or No result statements.